Explore the pervasive threat of PFAS contamination and its impact on health. Learn about the risks, sources, and preventive measures against these harmful chemicals. Stay informed for a healthier future. - Tweet this post or save it as it has a ton of info you may want to circle back to from time to time.
Chapter 1. Understanding PFAS Contamination
1.1. Introduction to PFAS Chemicals
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) represent a group of man-made chemicals characterized by their unique chemical structure, which includes fluorine atoms bonded to carbon chains. These chemicals have gained significant attention due to their widespread presence in various products and environments, including water sources, soil, and consumer goods.
Definition and Characteristics of PFAS
PFAS are highly durable and resistant to heat, water, and oil, making them ideal for use in a wide range of industrial and consumer applications. Their unique properties make them desirable for manufacturing products like non-stick cookware, stain-resistant fabrics, firefighting foams, and food packaging materials.
Sources of PFAS Contamination
PFAS contamination can originate from several sources, including industrial discharges, firefighting activities, landfills, and wastewater treatment plants. Additionally, PFAS can enter the environment through the disposal of consumer products containing these chemicals, as well as through atmospheric deposition.
1.2. Health Risks Associated with PFAS
Scientific research has established a clear link between PFAS exposure and a variety of serious health problems, posing significant risks to human health and the environment.
Link Between PFAS and Serious Health Problems
Exposure to PFAS has been associated with adverse health effects, including liver damage, immune system dysfunction, thyroid disease, and certain types of cancer. These chemicals can accumulate in the human body over time, leading to long-term health consequences.
Impact of PFAS on Human Health
PFAS exposure can occur through ingestion of contaminated food and water, inhalation of contaminated air, and dermal contact with consumer products. Vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women, infants, and individuals with compromised immune systems, may be at greater risk of adverse health effects from PFAS exposure.
Chapter 2. The Scope of PFAS Contamination
2.1. Nationwide Study on Drinking Water Contamination
Recent studies have revealed alarming levels of PFAS contamination in drinking water supplies across the United States, raising concerns about public health and environmental safety.
Overview of the Study's Findings
A comprehensive nationwide study conducted by environmental agencies and research institutions found that nearly half of the nation's drinking water sources contain detectable levels of PFAS chemicals. This widespread contamination underscores the urgent need for effective remediation strategies and regulatory action.
Significance of the Study's Results
The findings of the study highlight the extent of PFAS contamination and its potential implications for public health. The presence of these chemicals in drinking water sources underscores the need for stringent regulations and proactive measures to protect human health and the environment.
2.2. Presence of PFAS in Everyday Items
PFAS chemicals are pervasive in modern society, present in a wide range of everyday products and materials.
Common Products Containing PFAS
PFAS are commonly found in consumer products such as non-stick cookware, waterproof clothing, food packaging, and personal care products. These chemicals provide desirable properties such as water and stain resistance, but their widespread use has led to environmental contamination and human exposure.
Contribution of Consumer Goods to PFAS Contamination
The disposal and degradation of PFAS-containing products can release these chemicals into the environment, where they can persist for extended periods. As a result, PFAS contamination has become a significant environmental and public health concern, prompting efforts to mitigate exposure and contamination.
Chapter 3. Remediation Technologies for PFAS
3.1. Emerging Technologies for PFAS Removal
In response to the growing threat of PFAS contamination, researchers and environmental engineers have developed innovative technologies for the remediation of PFAS-contaminated water and soil.
Advancements in Water Treatment Methods
Recent advancements in water treatment technology have led to the development of specialized filtration systems and chemical processes capable of removing PFAS from contaminated water sources. These technologies offer promising solutions for addressing PFAS contamination in drinking water supplies and industrial wastewater.
Effectiveness of New Remediation Techniques
Laboratory and field studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of emerging PFAS remediation techniques, including activated carbon adsorption, ion exchange, and advanced oxidation processes. These methods have shown promising results in removing PFAS compounds from water and soil, offering hope for the mitigation of PFAS contamination in affected areas.
3.2. Case Study: PFAS Remediation Facility in Grand Rapids
One notable example of PFAS remediation efforts is the establishment of a state-of-the-art treatment facility in Grand Rapids, Michigan.
Overview of the Facility's Operations
The PFAS remediation facility in Grand Rapids employs advanced treatment technologies to remove PFAS contaminants from drinking water sources. Using a combination of filtration, chemical treatment, and advanced oxidation processes, the facility has successfully reduced PFAS levels in treated water to below regulatory limits.
Successes and Challenges in PFAS Removal
While the Grand Rapids facility has achieved significant success in PFAS remediation, challenges remain in scaling up these technologies for widespread implementation. Factors such as cost, energy consumption, and treatment efficiency must be carefully considered to ensure the long-term sustainability of PFAS remediation efforts.
Chapter 4. Implications and Regulatory Framework
4.1. Environmental and Public Health Implications
The widespread presence of PFAS contaminants in the environment poses significant risks to ecosystems and human health.
Long-Term Effects of PFAS Contamination
PFAS chemicals are persistent in the environment and can bioaccumulate in the food chain, posing risks to wildlife and aquatic organisms. Long-term exposure to low levels of PFAS may have adverse effects on ecosystem health and biodiversity.
Community Concerns and Responses
Communities affected by PFAS contamination have voiced concerns about the health effects and environmental impacts of exposure to these chemicals. Public health agencies and environmental organizations play a crucial role in raising awareness, conducting research, and implementing strategies to address PFAS contamination and its consequences.
4.2. Regulatory Landscape for PFAS
Efforts to regulate PFAS contamination are underway at both the federal and state levels, aiming to establish standards and guidelines for PFAS exposure and remediation.
Federal vs. State Regulations
While the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed regulations for PFAS in drinking water, individual states have also implemented their own regulatory measures to address PFAS contamination. These regulations vary in scope and stringency, reflecting the diverse approaches to managing PFAS pollution at the state level.
Role of the EPA in Addressing PFAS Contamination
The EPA plays a central role in coordinating national efforts to address PFAS contamination and establish regulatory frameworks for PFAS management. Through research, monitoring, and enforcement activities, the EPA works to protect public health and the environment from the impacts of PFAS pollution.
Chapter 5. Conclusion and Future Outlook
5.1. Summary of Key Points
In summary, PFAS contamination represents a significant environmental and public health challenge, requiring coordinated efforts from government agencies, industry stakeholders, and the scientific community.
Recap of PFAS Contamination Issues
The widespread presence of PFAS contaminants in drinking water, consumer products, and the environment highlights the urgency of addressing PFAS pollution through targeted remediation efforts and regulatory action.
Importance of Continued Research and Action
Moving forward, continued research, innovation, and collaboration will be essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate PFAS contamination, protect human health, and safeguard the environment for future generations.
5.2. Future Directions in PFAS Remediation
Looking ahead, ongoing efforts to develop new remediation technologies, improve treatment efficiency, and enhance regulatory oversight will shape the future of PFAS management and pollution prevention.
Areas for Further Innovation and Development
Research priorities include the development of cost-effective, scalable PFAS remediation methods, as well as the assessment of long-term environmental impacts and ecosystem resilience in PFAS-affected areas.
Collaborative Efforts in Addressing PFAS Contamination
Collaboration among government agencies, academic institutions, industry partners, and community stakeholders will be crucial for addressing PFAS contamination comprehensively and implementing sustainable solutions for PFAS management and remediation.
Semantically Similar FAQs:
- What are the health risks associated with PFAS exposure?
- How can consumers protect themselves from PFAS contamination in drinking water?
- What steps can industries take to reduce PFAS emissions and contamination?
- Are there any natural methods for removing PFAS from water sources?
- How do PFAS regulations vary between different states in the U.S.?
Unveiling the Hidden Dangers: Tap Water Contamination and the Fight for Safe Drinking Water
In recent years, concerns about the quality of tap water in the United States have escalated, fueled by alarming revelations of contamination with toxic chemicals. A recent study conducted across 43 cities has shed light on a pervasive problem that threatens public health and environmental integrity. Let's delve into the intricacies of this issue and explore the efforts to combat it.
Understanding the Scope of Tap Water Contamination
The study, spearheaded by the Environmental Working Group, has uncovered disturbing findings regarding the presence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in tap water. These chemicals, commonly used in industrial processes and consumer products, have been linked to a myriad of health problems, including cancer and reproductive issues.
Cities Affected and the Human Impact
Among the affected cities are major urban centers like Miami, New Orleans, Philadelphia, Washington DC, and Chicago. The widespread contamination has dire implications for public health, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive action to address the crisis.
The Nexus with "Dark Waters" Film: A Tale of Corporate Accountability
The revelations of tap water contamination resonate eerily with the narrative depicted in the Hollywood film "Dark Waters." Directed by Todd Haynes, the film chronicles the real-life saga of attorney Rob Bilott's relentless pursuit of justice against corporate giant DuPont. Portrayed by actors such as Tim Robbins, Mark Ruffalo, and Anne Hathaway, the film serves as a stark reminder of the human cost of corporate negligence.
Chemical Usage and Environmental Fallout
DuPont's use of PFAS chemicals in the manufacturing of Teflon stands as a chilling testament to the environmental fallout of unchecked industrial practices. For over six decades, these chemicals have infiltrated ecosystems, contaminating water sources, soil, and even the bloodstreams of humans and animals worldwide.
The Legal Battle for Accountability
Rob Bilott's legal crusade against DuPont epitomizes the struggle for corporate accountability in the face of environmental injustice. From representing impacted individuals and communities in West Virginia to spearheading nationwide litigation efforts, Bilott's endeavors have catalyzed a broader movement for transparency and accountability.
Scientific Validation and Ongoing Efforts
Central to Bilott's legal strategy are rigorous scientific studies confirming the adverse health effects of PFAS exposure. Despite concerted efforts by regulatory agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to downplay the risks, independent research continues to underscore the urgency of addressing this public health crisis.
Advocacy, Awareness, and Collective Action
The intersection of media coverage and advocacy efforts has been instrumental in amplifying awareness of tap water contamination and its far-reaching consequences. Through platforms like "Dark Waters" and grassroots activism, communities are mobilizing to demand safeguards for clean, safe drinking water.
In conclusion, the scourge of tap water contamination underscores the imperative of vigilance, accountability, and collective action. As stewards of our environment and guardians of public health, we must remain steadfast in our commitment to safeguarding the most fundamental of human rights: access to clean water.
The Threat of PFAS Contamination: A Wake-Up Call for Maine's Agricultural Community
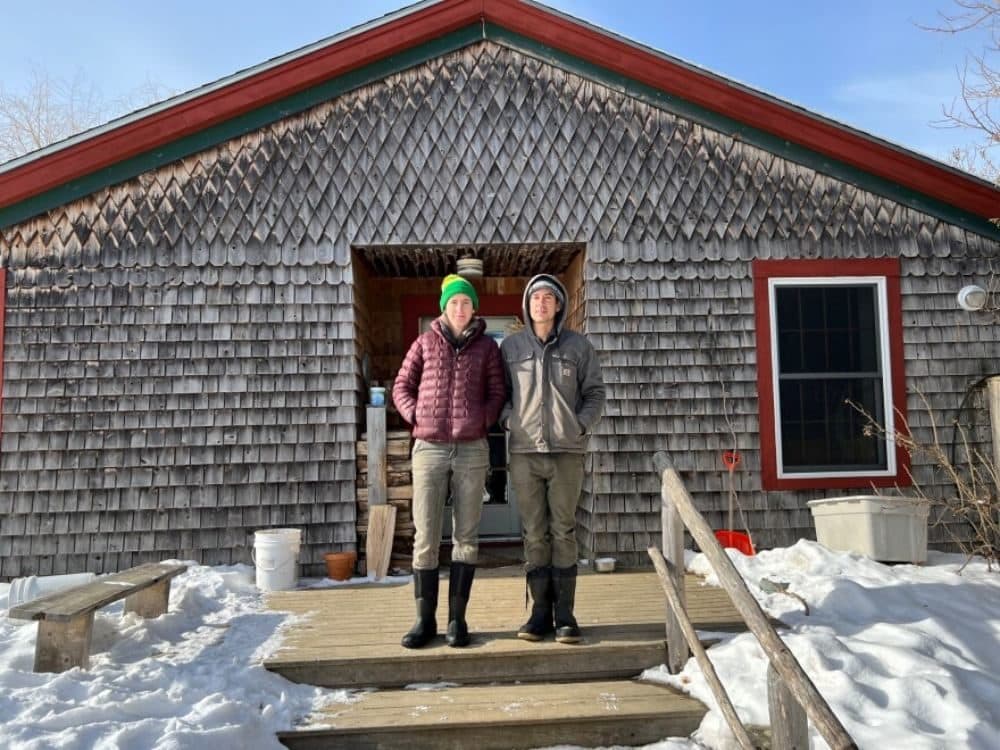
In the serene landscapes of Unity, Maine, where idyllic farms dot the countryside, a silent threat looms over the livelihoods of farmers. The story of Songbird Farm, nestled amidst snow-covered fields, unveils the harrowing reality of PFAS contamination and its profound impact on Maine's agriculture.
Unveiling the Crisis
Johanna Davis and Adam Nordell, the resilient faces behind Songbird Farm, epitomize the struggles faced by many farmers across Maine. Their aspirations to cultivate organic vegetables and grains were abruptly halted by the discovery of PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, in their soil and water.
The contamination traces back to decades-old practices of fertilizing farmlands with municipal sludge, a practice endorsed by regulatory agencies. However, the repercussions of these actions now haunt the very communities they were meant to nourish.
The Perils of PFAS
PFAS, aptly termed "forever chemicals," embody their moniker by persisting in the environment long after their initial use. These insidious compounds infiltrate soil, water, and even find their way into the food chain, posing significant health risks to both humans and ecosystems.
Studies link PFAS exposure to an array of health ailments, including cancer, kidney dysfunction, and adverse birth outcomes. The alarming levels of PFAS found at Songbird Farm serve as a stark reminder of the invisible threats lurking in our midst.
State of Emergency
Maine's agricultural landscape is under siege as PFAS contamination spreads its tentacles far and wide. The state's Department of Environmental Protection spearheads an ambitious testing campaign, aiming to assess over 700 sites for PFAS presence.
The repercussions reverberate beyond farmlands, infiltrating the very essence of communities built on trust and sustainability. Dairy farms shutter their operations, organic produce is pulled from shelves, and the specter of uncertainty looms large over farmers and consumers alike.
Call to Action
As Maine grapples with the PFAS crisis, a collective call to action emerges. Stakeholders, from government agencies to grassroots organizations, must collaborate to mitigate the fallout and safeguard the future of agriculture.
Financial support, regulatory reforms, and robust testing protocols are imperative to address the multifaceted challenges posed by PFAS contamination. Moreover, prioritizing transparency and consumer trust fosters resilience in the face of adversity.
Source: https://www.wbur.org/news/2022/02/08/pfas-forever-chemicals-crisis-maine-agriculture
Looking Ahead
The plight of Songbird Farm serves as a poignant reminder of the fragility of our agricultural systems. Yet, amidst adversity lies the seeds of resilience and renewal. By championing sustainable practices and advocating for comprehensive solutions, Maine's farming community charts a course towards a brighter, PFAS-free future.
Unveiling the Truth: Testing Yard Waste Bags for PFAS Contamination
In today's eco-conscious world, understanding the environmental impact of everyday items is crucial. Recently, the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (MPCA) conducted extensive tests on yard waste bags to evaluate the presence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Let's delve into the findings and their implications for environmental sustainability.
Assessing PFAS in Yard Waste Bags
The MPCA's investigation involved testing sixteen yard waste bags using sophisticated methods such as Total Oxidizable Precursor (TOP) and Total Organic Fluorine (TOF) analysis. These tests aimed to determine the extent of PFAS contamination in commonly used yard waste bags.
Key Findings
-
Absence of Intentional PFAS Addition: Encouragingly, none of the tested yard waste bags contained intentionally added PFAS above the BPI Certified compostable product limit of 100 ppm.
-
Minor Contribution to PFAS: Yard waste bags were identified as minor contributors of PFAS compared to other sources in composting operations. This suggests that while they may contain traces of PFAS, their overall impact is relatively low.
-
Varied Levels of Total Organic Fluorine: Half of the samples exhibited Total Organic Fluorine levels ranging from 9 to 49 ppm. This variability underscores the need for manufacturers to monitor and reduce PFAS content in yard waste bags.
Implications and Recommendations
The findings from MPCA's study shed light on the complex relationship between yard waste bags and PFAS contamination. While the results are reassuring in terms of intentional PFAS addition, there are several implications and recommendations to consider:
-
Environmental Impact: Understanding the presence of PFAS in yard waste bags is essential for mitigating environmental contamination and protecting ecosystems.
-
Manufacturer Responsibility: Manufacturers should prioritize monitoring and reducing PFAS content in yard waste bags to minimize environmental impact and ensure compliance with certification standards.
-
Research and Sensitivity Improvements: Further research and sensitivity improvements in testing methods are necessary to enhance our understanding of PFAS contamination in various environmental settings.
The MPCA's initiative to test yard waste bags for PFAS contamination represents a significant step towards environmental stewardship and sustainability. By unraveling the complexities of PFAS presence in everyday products, we can make informed decisions to safeguard our environment for future generations.
On a facebook compost group:
These chemicals are, on a human life timeframe, permanent in our environment. They will eventually break down, but at the rate we're going, we may not, as a species, be around to see that happen. There are over 4700 chemicals in this group... All man-made.
One of their properties is making paper very water resistant, which is why leaf collection bags don't break apart when they get wet and heavy. In our area plastic bags are illegal for leaf/garden waste. People must use the paper bags or the leaves are not picked up. Last year I gathered 125 bags of leaves from my community. The leaves are Garden Gold, but the bags are toxic, although my research days the level of PFAS chemicals is within safe limits. When a chemical is permanent, it will bioaccumulate, so I don't see how any level can be considered safe. So what to do with all those bags going forward???? Burn them in my wood stove (AI query says wood stove may not attain temperatures hot enough for long enough to completely break them down)??? Compost them??? Send them to the landfill???
My first introduction to these chemicals was through an article about PFAS getting into farmers' field and then into the ground water system in New England area of USA. The farms and water are now so toxic that it's illegal to grow/sell food on those farms and the water is unsafe to drink... so the farmers have lost their life work!!! The chemicals came into their system through municipal sewage treated with PFAS and then spread on their land. This is about as frightening a scenario as one could imagine... the stuff of sci-fi horror movies .. except it's not a movie!!!
https://www.facebook.com/groups/520291265993619
-
What are PFAS?
- PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of man-made chemicals that have been widely used in various industrial and consumer products for decades.
- PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of man-made chemicals that have been widely used in various industrial and consumer products for decades.
-
Where are PFAS found?
- PFAS can be found in a wide range of products, including firefighting foams, non-stick cookware, waterproof clothing, food packaging, and certain types of carpets and textiles.
- PFAS can be found in a wide range of products, including firefighting foams, non-stick cookware, waterproof clothing, food packaging, and certain types of carpets and textiles.
-
What are the health effects of PFAS exposure?
- Exposure to PFAS has been linked to numerous adverse health effects, including increased cholesterol levels, thyroid disease, decreased fertility, and an increased risk of certain cancers, such as kidney and testicular cancer.
- Exposure to PFAS has been linked to numerous adverse health effects, including increased cholesterol levels, thyroid disease, decreased fertility, and an increased risk of certain cancers, such as kidney and testicular cancer.
-
How do PFAS contaminate water sources?
- PFAS can enter water sources through various means, including industrial discharges, runoff from firefighting training areas, and the use of PFAS-containing products that leach into the environment.
- PFAS can enter water sources through various means, including industrial discharges, runoff from firefighting training areas, and the use of PFAS-containing products that leach into the environment.
-
How can I reduce my exposure to PFAS?
- To reduce exposure to PFAS, individuals can avoid products containing PFAS, such as non-stick cookware and stain-resistant fabrics, and opt for alternatives whenever possible. Additionally, using a water filtration system certified to remove PFAS can help reduce exposure through drinking water.
- To reduce exposure to PFAS, individuals can avoid products containing PFAS, such as non-stick cookware and stain-resistant fabrics, and opt for alternatives whenever possible. Additionally, using a water filtration system certified to remove PFAS can help reduce exposure through drinking water.
-
Are there regulations in place to limit PFAS exposure?
- While regulatory agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have established health advisory levels for certain PFAS in drinking water, there are currently no federal regulations specifically targeting PFAS contamination.
- While regulatory agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have established health advisory levels for certain PFAS in drinking water, there are currently no federal regulations specifically targeting PFAS contamination.
-
What are the challenges in cleaning up PFAS contamination?
- PFAS are known as "forever chemicals" because they persist in the environment and accumulate in the bodies of humans and animals. Cleaning up PFAS contamination poses significant challenges due to their widespread distribution and resistance to degradation.
- PFAS are known as "forever chemicals" because they persist in the environment and accumulate in the bodies of humans and animals. Cleaning up PFAS contamination poses significant challenges due to their widespread distribution and resistance to degradation.
-
What role do PFAS play in firefighting foams?
- PFAS are commonly used in firefighting foams due to their ability to extinguish flammable liquid fires effectively. However, the use of PFAS-containing firefighting foams has contributed to environmental contamination in areas where they have been used.
- PFAS are commonly used in firefighting foams due to their ability to extinguish flammable liquid fires effectively. However, the use of PFAS-containing firefighting foams has contributed to environmental contamination in areas where they have been used.
-
Are there alternatives to PFAS-containing products?
- Yes, there are alternatives to PFAS-containing products available on the market. For example, manufacturers are developing non-stick coatings and waterproofing treatments that use alternative materials to PFAS.
- Yes, there are alternatives to PFAS-containing products available on the market. For example, manufacturers are developing non-stick coatings and waterproofing treatments that use alternative materials to PFAS.
-
What research is being done to better understand PFAS and their effects?
- Scientists and researchers continue to study PFAS to better understand their environmental fate, health effects, and potential remediation methods. This research is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate PFAS contamination and protect public health.